题目地址
https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/description/
题目描述
Given a non-empty array containing only positive integers, find if the array can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both subsets is equal.
Note:
Each of the array element will not exceed 100.
The array size will not exceed 200.
Example 1:
Input: [1, 5, 11, 5]
Output: true
Explanation: The array can be partitioned as [1, 5, 5] and [11].
Example 2:
Input: [1, 2, 3, 5]
Output: false
Explanation: The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum subsets.
思路
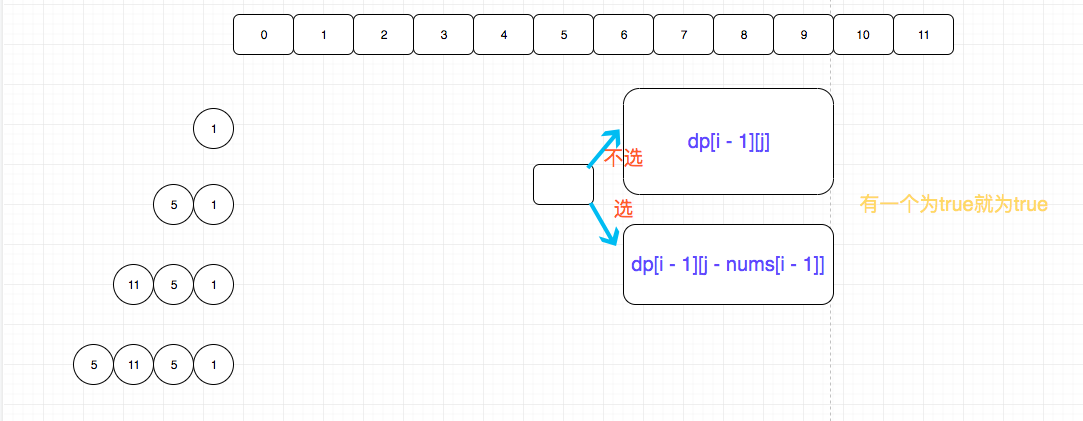
题目要求给定一个数组, 问是否能划分为和相等的两个数组。
这是一个典型的背包问题,我们可以遍历数组,对于每一个,我们都分两种情况考虑,拿或者不拿。
背包问题处理这种离散的可以划分子问题解决的问题很有用。
如果能够识别出这是一道背包问题,那么就相对容易了。
关键点解析
- 背包问题
代码
/*
* @lc app=leetcode id=416 lang=javascript
*
* [416] Partition Equal Subset Sum
*
* https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/description/
*
* algorithms
* Medium (39.97%)
* Total Accepted: 79.7K
* Total Submissions: 198.5K
* Testcase Example: '[1,5,11,5]'
*
* Given a non-empty array containing only positive integers, find if the array
* can be partitioned into two subsets such that the sum of elements in both
* subsets is equal.
*
* Note:
*
*
* Each of the array element will not exceed 100.
* The array size will not exceed 200.
*
*
*
*
* Example 1:
*
*
* Input: [1, 5, 11, 5]
*
* Output: true
*
* Explanation: The array can be partitioned as [1, 5, 5] and [11].
*
*
*
*
* Example 2:
*
*
* Input: [1, 2, 3, 5]
*
* Output: false
*
* Explanation: The array cannot be partitioned into equal sum subsets.
*
*
*
*
*/
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {boolean}
*/
var canPartition = function(nums) {
let sum = 0;
for(let num of nums) {
sum += num;
}
if (sum & 1 === 1) return false;
const half = sum >> 1;
let dp = Array(half);
dp[0] = [true, ...Array(nums.length).fill(false)];
for(let i = 1; i < nums.length + 1; i++) {
dp[i] = [true, ...Array(half).fill(false)];
for(let j = 1; j < half + 1; j++) {
if (j >= nums[i - 1]) {
dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] || dp[i - 1][j - nums[i - 1]];
}
}
}
return dp[nums.length][half]
};
书籍推荐