集合
list set map 泛型 工具 树 基数排序 栈,队列,链表 冒泡排序 快速排序 堆排序 递归
对象用于封装数据,对象多了需要存储,如果对象的个数不确定,就是用集合容器进行存储
- 用于存储对象的容器
- 集合的长度可变
- 不可以存储基本类型数据
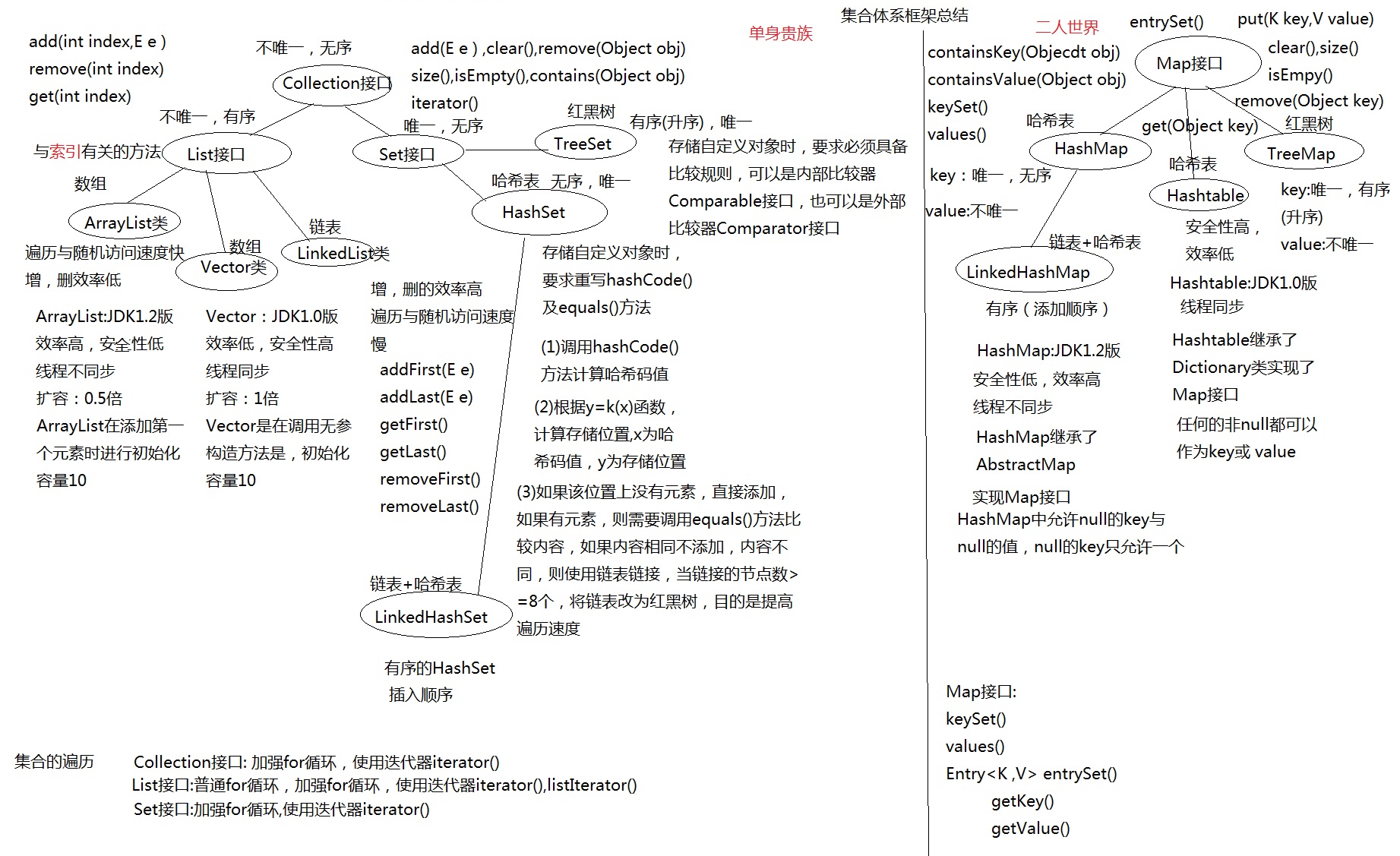
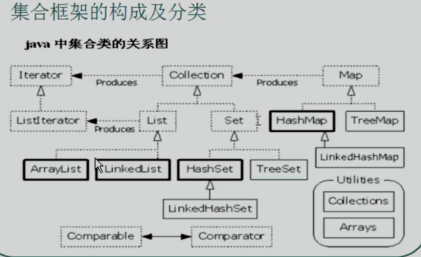
集合容器因为内部数据结构不同,有多种容器,不断的向上抽取,就形成了集合框架
Collection
常见方法
-
添加 boolean add(Object obj) boolean addAll(Collection coll)
-
删除 boolean remove(Object obj) boolean removeAll(Collection coll) void clear();
-
查询 boolean contains(Object obj) boolean containsAll(Collection coll) boolean isEmpty() int size() Iterator iterator() 迭代器 返回一个对象,必须依赖于具体的容器,因为容器的数据结构不同, 所以该迭代器对象是在容器中进行内部实现的内部类。
对于使用容器者而言,具体的实现不重要,只要通过容器获取该实现的迭代器的对象即可,也就是iterator()方法。
Iterator就是容器取出数据的公共接口
-
其他 Object[] toArray() boolean retainAll(Collection coll) 取交集
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add("abc1");
coll.add("abc2");
coll.add("abc3");
System.out.println(coll); //[abc1, abc2, abc3]
coll.remove("abc3");
System.out.println(coll); //[abc1, abc2]
System.out.println(coll.contains("abc3")); //false
System.out.println(coll.size()); //2
System.out.println(coll.isEmpty()); //false
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(coll.toArray())); //[abc1, abc2]
Collection c1 = new ArrayList();
Collection c2 = new ArrayList();
c1.add("a1");
c1.add("a2");
c1.add("a3");
c2.add("a2");
c2.add("a3");
c2.add("a4");
// c1.addAll(c2);
// System.out.println(c1); //[a1, a2, a3, a2, a3, a4]
// c1.removeAll(c2);
// System.out.println(c1); //[a1] 删除交集
// c1.retainAll(c2);
// System.out.println(c1); //[a2, a3] 取交集
// System.out.println(c1.containsAll(c2)); //false
// Iterator it = c1.iterator();
// while(it.hasNext()){
// System.out.println(it.next()); //a1 a2 a3
// }
for(Iterator it =c1.iterator(); it.hasNext();){
System.out.println(it.next()); //a1 a2 a3
}
List和Set
- List:有序,元素都有索引,可以重复
- Set:无序,不能重复
书籍推荐