IO流
File
构造函数
public File(String pathname) //文件的绝对路径
public File(URI uri) //文件的URI地址
public File(String parent, String child) //指定父文件绝对路径、子文件绝对路径
public File(File parent, String child) //指定父文件、子文件相对路径
//下面这两个是File类中私有的构造函数,外面不能调用
private File(String child, File parent)
private File(String pathname, int prefixLength)
boolean file.mkdirs() // 创建目录
boolean file.createNewFile() // 创建文件
boolean file.exists() //文件是否存在
boolean file.isFile() //是否是文件
boolean file.isDirectory() //是否是目录
boolean file.isHidden() //是否隐藏
boolean file.isAbsolute() //是否为绝对路径
boolean file.canRead() //是否可读
boolean file.canWrite() //是否可写
boolean file.canExecute() //是否可执行
String file.getName() //获取文件的名字,只是名字,没有路径
String file.getParent() //获取父目录的绝对路径,返回值是一个字符串。如果文件有父目录,那么返回父目录的绝对路径,(比如:`E:\cat`) , 如果文件本身就在磁盘的根目录,那么返回磁盘的路径,(比如:`E:\`)。
File file.getParentFile() //获取父文件,返回值是一个File对象。
long time = file.lastModified() ; //返回文件最后一次修改的时间
Date dt = new Date(time);
boolean renameTo(File file) //文件命名
long file.length() //返回文件的大小,单位字节
boolean file.delete() //删除文件
String[] file.list() //获取该目录下的所有的文件的名字。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有文件的名字,只是名字,不含路径;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`list()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。
File[] file.listFiles() //获取该目录下的所有的文件。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有的文件 ;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`listFiles()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。
基本操作
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String path = "d:/a.txt";
//构建File对象
File file = new File(path);
File file2 = new File("d:/","a.txt");
System.out.println(file.length());
//路径
System.out.println(System.getProperty("user.dir"));
//E:\my-github\practice\java\bz\MyProject
file = new File("a.txt"); //不存在也可以构建file对象
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
//E:\my-github\practice\java\bz\MyProject\a.txt
testFileApi();
testDirApi();
}
private static void testFileApi() throws IOException {
String path = "d:/a.txt";
File file = new File(path);
File file2 = new File("a.txt");
//基本信息
System.out.println(file.getName()); //a.txt
System.out.println(file.getPath()); //d:\a.txt 路径是什么就是什么
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath()); //d:\a.txt 永远是绝对路径
System.out.println(file.getParent()); //d:\
//状态
System.out.println(file.exists()); //true
System.out.println(file.isFile()); //true
System.out.println(file.isDirectory()); //false
System.out.println(file2.exists()); //false
System.out.println(file2.isFile()); //false
System.out.println(file2.isDirectory()); //false
System.out.println(file.length()); //7 文件不存在或是文件夹,这个length的长度为0
boolean flag = file2.createNewFile(); //不存在则创建
System.out.println(flag); //true
flag = file2.delete();
System.out.println(flag); //true 删除已经存在的
}
/*
* mkdir 上级目录不存在则报错
* mkdirs 上级目录可以不存在,不存在则一同创建
*/
private static void testDirApi() {
File dir = new File("d:/b");
boolean flag = dir.mkdirs();
System.out.println(flag);
System.out.println("---------------------");
File dirFile = new File("E:\\my-github\\my-java");
String[] names = dirFile.list();
for (String string : names) {
System.out.println(string);
}
System.out.println("---------------------");
File[] files = dirFile.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
}
遍历目录
public class FilesTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义遍历目录
File file = new File("G:\\test\\my-java");
PrintFiles(file, 0);
}
public static void PrintFiles(File file, int level) {
//打印分隔符
for(int i=0;i<level;i++) {
System.out.print("-");
}
//打印文件名
System.out.println(file.getName());
//判断是否是目录
if(file.isDirectory()) {
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
//递归遍历
PrintFiles(f, level+1);
}
}
}
}
编码 解码 乱码
//编码就是字符串转为字节,解码就是字转为字符串
String msgString = "性命生命使命";
//编码
byte[] datas = msgString.getBytes(); //默认使用工程字符集
System.out.println(datas.length); //18 UTF-8 每个汉字3个字节
// datas = msgString.getBytes("GBK");
// System.out.println(datas.length); //12 GBK 每个孩子2个字节
//解码
String string = new String(datas,0,datas.length,"utf8");
System.out.println(string);
//乱码原因
//1 字节数不够
String string1 = new String(datas,0,datas.length-2,"utf8");
System.out.println(string1); //性命生命使�
//1 字符集不同
String string2 = new String(datas,0,datas.length-2,"gbk");
System.out.println(string2); //鎬у懡鐢熷懡浣垮
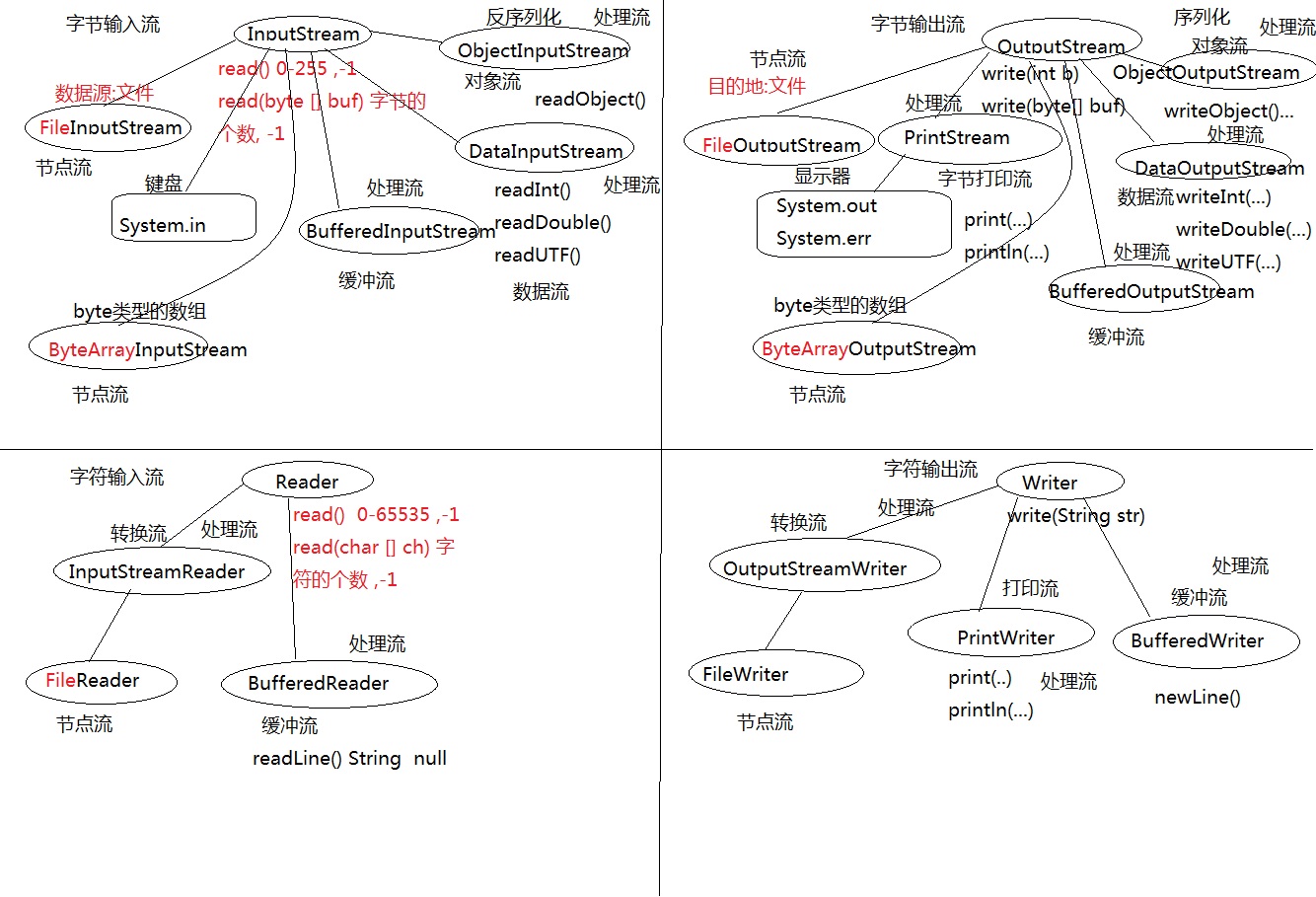
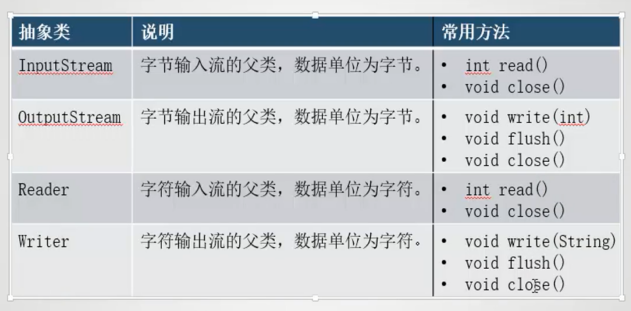
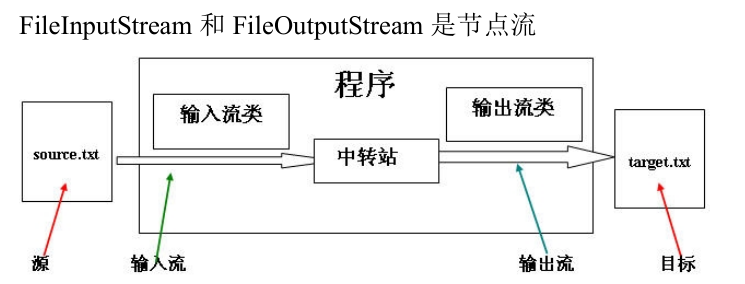
IO流
只要是考虑处理纯文本,就用字符流,其他时候都用字节流
特点
close flush两个重要的方法
流操作四部曲
- 源
- 选择流
- 操作
- 释放
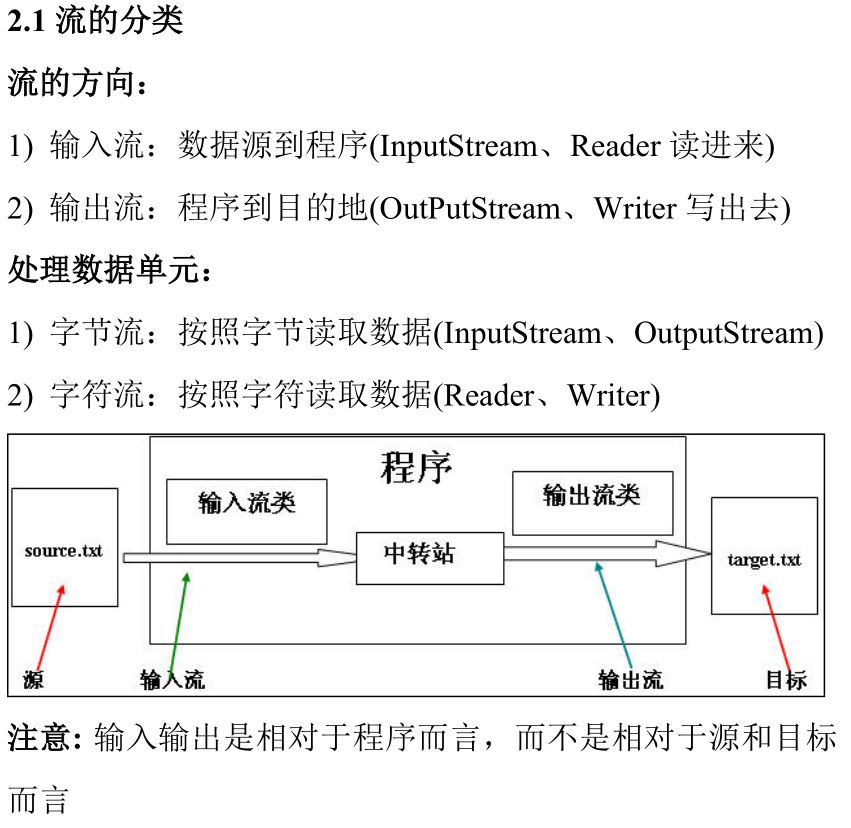
流的分类
字节流和字符流 stream reader/write 输入流和输出流 节点流和处理流
节点流(输入输出流):
父 类 :InputStream 、OutputStream、 Reader、 Writer
文 件 :FileInputStream 、 FileOutputStream 、FileReader 、FileWriter
数 组 :ByteArrayInputStream、 ByteArrayOutputStream、 CharArrayReader 、CharArrayWriter
字符串 :StringReader、 StringWriter
管 道 :PipedInputStream 、PipedOutputStream 、PipedReader 、PipedWriter
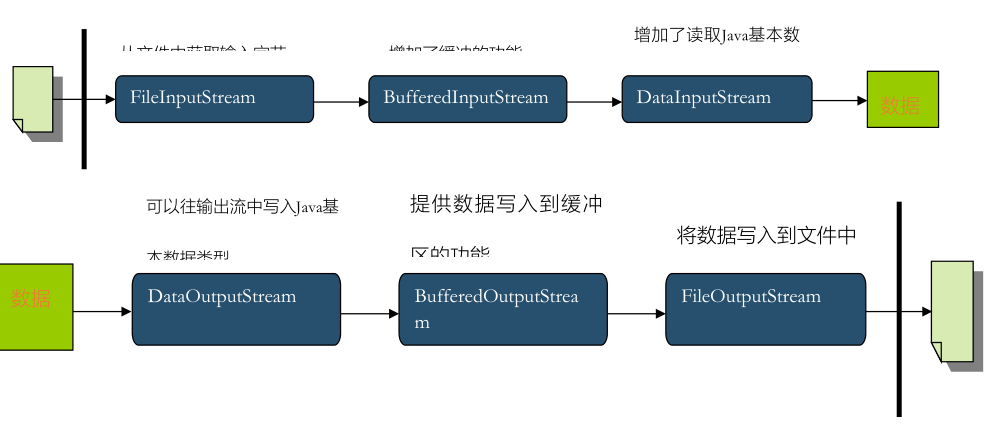
处理流:
缓冲流:BufferedInputStream 、BufferedOutputStream、 BufferedReader、 BufferedWriter
转换流:InputStreamReader 、OutputStreamReader
数据流: DataInputStream 、DataOutputStream
转换流
InputStreamReader(InputStream); //通过构造函数初始化,使用的是本系统默认的编码表GBK。
InputStreamWriter(InputStream,String charSet); //通过该构造函数初始化,可以指定编码表。
OutputStreamWriter(OutputStream); //通过该构造函数初始化,使用的是本系统默认的编码表GBK。
OutputStreamwriter(OutputStream,String charSet); //通过该构造函数初始化,可以指定编码表。
字节流
字符流和字节流复制
public static void byteHandle() throws IOException {
//创建源
File ifile = new File("d:/1.psd");
File oFile = new File("d:/2.psd");
//选择流
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(ifile);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(oFile);
//操作
int temp=0;
int len=0; //每次实际接收长度
byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; //缓冲容器 每次循环可以接收长度
// while((temp=is.read())!=-1) {
// System.out.print((char)temp);
// }
while((len=is.read(buf))!=-1) {
//System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
//写出
os.write(buf,0,len);
os.flush();
}
//释放
if(null!=is) {
is.close();
}
if(null!=os) {
os.close();
}
}
public static void CharHandle() throws IOException {
File ifile = new File("d:/a.txt");
File oFile = new File("d:/c.txt");
Reader reader = new FileReader(ifile);
Writer writer = new FileWriter(oFile);
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = -1;
while((len=reader.read(chars))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,len));
writer.write(chars,0,len);
writer.flush();
}
if(null!=writer) {
reader.close();
}
if(null!=writer) {
writer.close();
}
}
//写入文件
FileOutputStream fisOutputStream = null;
try {
//true代表append
fisOutputStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt",true);
fisOutputStream.write(97);
byte[] bytes = "helloworld".getBytes();
fisOutputStream.write(bytes);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
if(fisOutputStream!=null)
fisOutputStream.close();
}
//读取单个字节,中转站是int,由于byte和char位数不同,缓冲区大小不同,所以中文会乱码,只有只用bytes或者缓冲流才能解决
FileInputStream fisInputStream = null;
fisInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.txt");
int count = fisInputStream.available();
System.out.println(count);
int buf=0;
int i =0;
//因为fisInputStream.read()会不断读取,所以这里先赋值给buf,避免在循环里获取不到原先的值
while((buf=fisInputStream.read())!=-1) {
i++;
System.out.print((char)buf);
}
fisInputStream.close();
System.out.println(i);
//读入到bytes 中转站是byte[] 缓冲区足够大,就不会乱码
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\a.txt");
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fileInputStream.read(bytes))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
fileInputStream.close();
//字节流复制文件
public static void copyFile(String fileSrc,String fileDesc) throws IOException {
FileInputStream srcStream = new FileInputStream(fileSrc);
FileOutputStream descStream = new FileOutputStream(fileDesc);
byte[] bytes = new byte[srcStream.available()];
int len = 0;
while((len=srcStream.read(bytes))!=-1) {
descStream.write(bytes,0,len);
}
descStream.close();
srcStream.close();
}
字符流
//读取单个字符,不会乱码,因为字符可以存储汉字
FileReader fileReader = null;
fileReader = new FileReader("d:\\a.txt");
int buf=0;
int i =0;
while((buf=fileReader.read())!=-1) {
i++;
System.out.print((char)buf);
}
fileReader.close();
System.out.println(i);
//读写chars
FileReader fileReaderByte = new FileReader("d:\\a.txt");
FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter("d:\\b.txt");
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=fileReaderByte.read(chars))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,len));
fileWriter.write(chars,0,len);
}
fileWriter.close();
fileReaderByte.close();
字节数组流
写入是写入到内存中,所以需要toByteArray取出
//创建源
byte[] src = "talk is cheap show me the code".getBytes();
byte[] dest=null;
//选择流
InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(src);
ByteArrayOutputStream os = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
//操作
int temp=0;
int len=0; //每次实际接收长度
byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; //缓冲容器 每次循环可以接收长度
while((len=is.read(buf))!=-1) {
System.out.println(new String(buf,0,len));
os.write(buf,0,len);
os.flush();
}
dest = os.toByteArray();
System.out.println(dest.length);
//释放
if(null!=is) {
is.close();
}
if(null!=os) {
os.close();
}
字节数组流拷贝图片
public static byte[] imageToByteArray(String path) throws IOException {
File file = new File(path);
byte[] dest = null;
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file);
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=is.read(buf))!=-1) {
baos.write(buf,0,len);
}
baos.flush();
if(null!=is) {
is.close();
}
return baos.toByteArray();
}
public static void byteArrayToImage(byte[] bytes, String path) throws IOException {
File destFile = new File(path);
InputStream is = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
OutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(destFile);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=is.read(buf))!=-1) {
fos.write(buf,0,len);
fos.flush();
}
if(null!=is) {
is.close();
}
if(null!=fos) {
fos.close();
}
}
释放资源
public static void copyFile(File rFile, File pFile) {
//Try-with-resources
try(InputStream is = new FileInputStream(rFile);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(pFile);) {
int temp = 0;
int len = 0; // 每次实际接收长度
byte[] buf = new byte[1024]; // 缓冲容器 每次循环可以接收长度
while ((len = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
os.write(buf, 0, len);
os.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*
* 释放资源
*/
public static void closeStream(Closeable... io) {
for (Closeable closeable : io) {
if (null != io) {
try {
closeable.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
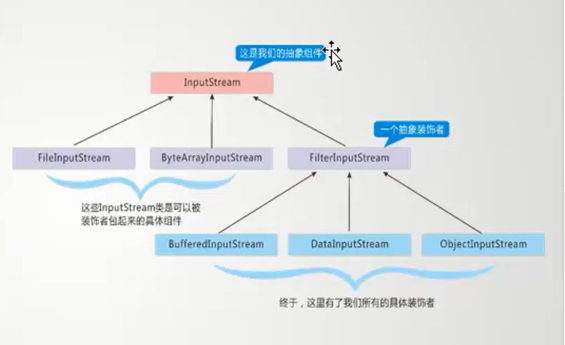
装饰器
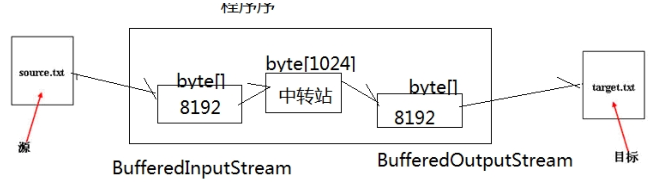
缓冲流
BufferedInputStream 和 BufferedOutputStream 是处理流(包装 流) BufferedReader readLine() 读取一个文本行的数据 BufferedWriter newLine();写入一个行分隔符。 使用缓冲字符流是复制文本文件常用的方式
- 读文件和写文件都使用了缓冲区,减少了读写次数,从而 提高了效率
- 当创建这两个缓冲流的对象时时,会创建了内部缓冲数组, 缺省使用 32 字节大小的缓冲区.
- 当读取数据时,数据按块读入缓冲区,其后的读操作则直 接访问缓冲区
- 当写入数据时,首先写入缓冲区,当缓冲区满时,其中的 数据写入所连接的输出流。使用方法 flush()可以强制将缓 冲区的内容全部写入输出流
- 关闭流的顺序和打开流的顺序相反.只要关闭高层流即可, 关闭高层流其实关闭的底层节点流 Flush 的使用:手动将 buffer 中内容写入文件
缓冲流读写字符串有优势,有 nextline
//字符缓冲
FileReader fReader = new FileReader("d:\\test.txt");
FileWriter fWriter = new FileWriter("d:\\test2.txt");
BufferedReader bReader = new BufferedReader(fReader);
BufferedWriter bWriter = new BufferedWriter(fWriter);
String line = null;
char[] chars = new char[1024];
int len=0;
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
while((line=bReader.readLine())!=null) {
bWriter.write(line);
bWriter.newLine();
}
// while((len=fReader.read(chars))!=-1) {
// fWriter.write(chars, 0, len);
// }
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start); //57
bWriter.close();
bReader.close();
//字节缓冲
BufferedInputStream bReader = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\\jdkhelp.CHM"));
BufferedOutputStream bWriter = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\\jdkhelp2.CHM"));
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=bReader.read(bytes))!=-1) {
bWriter.write(bytes,0,len);
bWriter.flush();
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
bWriter.close();
bReader.close();
BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
我们有必要知道不带缓冲的操作,每读一个字节就要写入一个字节,由于涉及磁盘的IO操作相比内存的操作要慢很多,所以不带缓冲的流效率很低。带缓冲的流,可以一次读很多字节,但不向磁盘中写入,只是先放到内存里。等凑够了缓冲区大小的时候一次性写入磁盘,这种方式可以减少磁盘操作次数,速度就会提高很多!
BufferedInputStream API
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in) //使用默认buf大小、底层字节输入流构建bis
BufferedInputStream(InputStream in, int size) //使用指定buf大小、底层字节输入流构建bis
int available(); //返回底层流对应的源中有效可供读取的字节数
void close(); //关闭此流、释放与此流有关的所有资源
boolean markSupport(); //查看此流是否支持mark
void mark(int readLimit); //标记当前buf中读取下一个字节的下标
int read(); //读取buf中下一个字节
int read(byte[] b, int off, int len); //读取buf中下一个字节
void reset(); //重置最后一次调用mark标记的buf中的位子
long skip(long n); //跳过n个字节、 不仅仅是buf中的有效字节、也包括in的源中的字节
BufferedOutputStream API
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out); //使用默认大小、底层字节输出流构造bos。默认缓冲大小是 8192 字节( 8KB )
BufferedOutputStream(OutputStream out, int size); //使用指定大小、底层字节输出流构造bos
void flush(); 将写入bos中的数据flush到out指定的目的地中、注意这里不是flush到out中、因为其内部又调用了out.flush()
write(byte b); 将一个字节写入到buf中
write(byte[] b, int off, int len); 将b的一部分写入buf中
在使用了缓冲流的情况下,只需要关闭缓冲流,不需要再关闭输入输出流
BufferedReader
BufferedReader(Reader in, int sz) //创建一个使用指定大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
BufferedReader(Reader in) //创建一个使用默认大小输入缓冲区的缓冲字符输入流。
int read() //读取单个字符。
int read(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) //将字符读入数组的某一部分。
String readLine() //读取一个文本行。
boolean ready() //判断此流是否已准备好被读取。
void reset() //将流重置到最新的标记。
long skip(long n) //跳过字符。
void close() //关闭该流并释放与之关联的所有资源。
void mark(int readAheadLimit) //标记流中的当前位置。
boolean markSupported() //判断此流是否支持 mark() 操作(它一定支持)。
BufferedWriter
BufferedWriter(Writer out, int sz) //创建一个使用给定大小输出缓冲区的新缓冲字符输出流。
BufferedWriter(Writer out) //建一个使用默认大小输出缓冲区的缓冲字符输出流。
void close() // 关闭此流,但要先刷新它。
void flush() //刷新该流的缓冲。
void newLine() //写入一个行分隔符。
void write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len) //写入字符数组的某一部分。
void write(int c) //写入单个字符。
void write(String s, int off, int len) //写入字符串的某一部分。
转换流
用于将字节流转化成字符流,字符流与字节流之间的桥梁 InputStreamReader 的作用是把 InputStream 转换成 Reader OutputStreamWriter 的作用是把 OutputStream 转换成 Writer
InputStream inputStream = System.in;
InputStreamReader iReader = new InputStreamReader(inputStream,"utf-8");
BufferedReader bReader = new BufferedReader(iReader);
BufferedWriter bWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream("d:\\a.txt"),"utf-8"));
String line = null;
while(!"over".equals(line=bReader.readLine())) {
bWriter.write(line);
bWriter.newLine();
bWriter.flush();
}
bWriter.close();
bReader.close();
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(BufferedReader isr =
new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new URL("http://www.baidu.com").openStream(),"UTF-8"));
BufferedWriter bw =
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("baidu.html"),"UTF-8"));
) {
String msg="";
while((msg=isr.readLine())!=null) {
bw.write(msg);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void getall() {
try(BufferedReader isr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter osw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
) {
String msgString="";
while(!msgString.equals("exit")) {
msgString=isr.readLine();
osw.write(msgString);
osw.newLine();
osw.flush();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
打印流
PrintStream 提供了一系列的 print()和 println(),可以实现 将基本数据类型格式化成字符串输出。对象类型将先调用 toString(),然后输出该方法返回的字符串
复制文件时可以使用PrintWriter代替BufferedWriter完成, 更简单
PrintStream pStream = System.out;
pStream.println(123);
FileReader fReader = new FileReader("d:\\test.txt");
BufferedReader bReader = new BufferedReader(fReader);
PrintWriter pWriter = new PrintWriter("d:\\test2.txt");
String line = null;
while((line=bReader.readLine())!=null) {
pWriter.print(line);
}
pWriter.close();
bReader.close();
PrintStream ps = System.out;
ps.println("123");
ps= new PrintStream(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/c.txt")),true);
ps.println("adfasf");
ps.println(true);
PrintWriter pw= new PrintWriter(new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:/d.txt")),true);
pw.println("efdasfdsgdsg");
pw.println(true);
数据流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//write();
read();
}
public static void read() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fStream = new FileInputStream("d:\\data.txt");
BufferedInputStream bStream = new BufferedInputStream(fStream);
DataInputStream dStream = new DataInputStream(bStream);
System.out.println(dStream.readUTF());
System.out.println(dStream.readInt());
System.out.println(dStream.readDouble());
System.out.println(dStream.readBoolean());
dStream.close();
}
public static void write() throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fStream = new FileOutputStream("d:\\data.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fStream);
DataOutputStream dStream = new DataOutputStream(bStream);
dStream.writeUTF("abc");
dStream.writeInt(97);
dStream.writeDouble(96.5);
dStream.writeBoolean(true);
dStream.close();
}
ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
BufferedOutputStream biStream = new BufferedOutputStream(bos);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(biStream);
dos.writeUTF("hello");
dos.writeInt(1);
dos.writeBoolean(false);
dos.flush();
byte[] arr = bos.toByteArray();
ByteArrayInputStream bas = new ByteArrayInputStream(arr);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(bas);
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(bis);
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
对象流
ObjectOutputStream > 序列化 > 写对象 , 将对象以 “二进 制/ 字节”的形式写到(文件) ObjectInputStream > 反序列化
将 Java 对象转换成字节序列(IO 字节流) 对象反序列化 (DeSerialization) 从字节序列中恢复 Java 对象
只有实现了 Serializable 接口的类的对象才可以被序列化
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//write();
read();
}
public static void read() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream oiStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("d:\\object.txt"));
System.out.println(oiStream.readInt());
System.out.println(oiStream.readBoolean());
Person p=(Person)oiStream.readObject();
System.err.println(p);
}
public static void write() throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream osStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("d:\\object.txt"));
osStream.writeInt(97);
osStream.writeBoolean(true);
osStream.writeObject(new Person("旺财",12));
}
序列化和反序列化
- 序列化能保存的元素 a) 只能保存对象的非静态成员变量 b) 不能保存任何成员方法和静态的成员变量 c) 不保存 transient 成员变量 d) 如果一个对象的成员变量是一个对象,这个对象的成 员变量也会保存 e) 串行化保存的只是变量的值,对于变量的任何修饰符, 都不能保存
- 使用对象流把一个对象写到文件时不仅保证该对象是序 列化的,而且该对象的成员对象也必须是可序列化的。
- 如果一个可序列化的对象包含对某个不可序列化的对象 的引用,那么整个序列化操作将会失败,并且会抛出一个 NotSerializableException。我们可以将这个引用标记为 transient,那么对象仍然可以序列化。 对象序列化注意事项
- 同一个对象多次序列化的处理 a) 所有保存到磁盘中的对象都有一个序列化编号 b) 序列化一个对象中,首先检查该对象是否已经序列化 过 c) 如果没有,进行序列化 d) 如果已经序列化,将不再重新序列化,而是输出编号 即可
- 如果不希望某些属性(敏感)序列化,或不希望出现递归 序列 a) 为属性添加 transient 关键字(完成排除在序列化之外) b) 自定义序列化(不仅可以决定哪些属性不参与序列化, 还可以定义属性具体如何序列化)
- 序列化版本不兼容 a) 修改了实例属性后,会影响版本号,从而导致反序列化 不成功 b) 解 决 方 案 : 为 Java 对 象 指 定 序 列 化 版 本 号 serialVersionUID
每次修改类之后, 最好都要手动修改serialVersionUID
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String fileStudent = "d:\\\\student.txt";
//write(fileStudent);
read(fileStudent); //Student [name=小强, age=12, pwd=null, className=null]
}
public static void read(String filePath) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
ObjectInputStream oisStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
Student student = (Student)oisStream.readObject();
System.out.println(student);
}
public static void write(String filePath) throws IOException {
ObjectOutputStream ooStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
Student student = new Student("小强", 12, "888888");
Student.setClassName("少年班");
ooStream.writeObject(student);
ooStream.close();
}
public class Student implements Serializable {
/**
* xuliehao
*/
private static final long serialVersionUID = 5226830560215252280L;
private String name;
private int age;
private static String className;
private transient String pwd;
private int sex;
public Student() {
super();
}
public Student(String name, int age, String pwd) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.pwd = pwd;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public static String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public static void setClassName(String className) {
Student.className = className;
}
public String getPwd() {
return pwd;
}
public void setPwd(String pwd) {
this.pwd = pwd;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + ", pwd=" + pwd + ", className=" + className + "]";
}
}
Commons IO
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//文件大小
long len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("d:/c.txt"));
//目录大小
len = FileUtils.sizeOf(new File("d:/"));
//遍历过滤文件
Collection<File> files = FileUtils.listFiles(
new File("E:\\my-github\\my-java"),
FileFilterUtils.and(new SuffixFileFilter("java"),EmptyFileFilter.NOT_EMPTY),
DirectoryFileFilter.INSTANCE);
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
//getAll();
//writeAll();
//copyAll();
}
//逐行读取
public static void getAll() throws IOException {
String msgString = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("d:/c.txt"),"utf-8");
System.out.println(msgString);
byte[] datas = FileUtils.readFileToByteArray(new File("d:/c.txt"));
System.out.println(datas.length);
List<String> msgs = FileUtils.readLines(new File("d:/c.txt"),"utf-8");
for (String string : msgs) {
System.out.println(string);
}
LineIterator it = FileUtils.lineIterator(new File("d:/c.txt"));
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.nextLine());
}
}
//写出内容
public static void writeAll() throws IOException {
FileUtils.write(new File("d:/c.txt"), "asfasfdasf","UTF-8",true);
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("d:/c.txt"), "asfasfdasf","UTF-8",true);
FileUtils.writeByteArrayToFile(new File("d:/c.txt"), "asfasfdasf".getBytes("UTF-8"),true);
List<String> datas = new ArrayList<String>();
datas.add("123");
datas.add("123");
datas.add("123");
FileUtils.writeLines(new File("d:/c.txt"), datas,",,,",true);
}
//复制文件
public static void copyAll() throws IOException{
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("d:/1.psd"), new File("d:/5.psd"));
FileUtils.copyFileToDirectory(new File("d:/1.psd"), new File("f:/"));
//FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("E:\\my-github\\my-java"), new File("F:/my-java"));
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL("https://minatest-1252830662.cos.ap-chengdu.myqcloud.com/mjmf/1555149783879.png"), new File("d:/man.png"));
String datas = IOUtils.toString(new URL("http://www.baidu.com"),"utf-8");
System.out.println(datas);
}