[轉] Android 非同步任務 - AsyncTask
本篇來介紹"非同步任務" - AsyncTask,我個人認為他比 Thread 配合 Handler 好用很多,因為他已經幫我們定義好方法,讓我們再處理前、後、中都可以去更新 UI 介面,而且也定義在各狀態下傳送資料的參數。 如果能夠好好的使用 AsyncTask,可以讓我們程式的可讀性增加,也更好管理。 首先,我們先介紹他的架構,如下:
class GoodTask extends AsyncTask<Void, Integer, String> {
// <傳入參數, 處理中更新介面參數, 處理後傳出參數>
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Void... arg0) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 再背景中處理的耗時工作
return null; // 會傳給 onPostExecute(String result) 的 String result
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPreExecute();
// 背景工作處理"前"需作的事
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
// 背景工作處理"中"更新的事
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPostExecute(result);
// 背景工作處理完"後"需作的事
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCancelled();
// 背景工作被"取消"時作的事,此時不作 onPostExecute(String result)
}
}
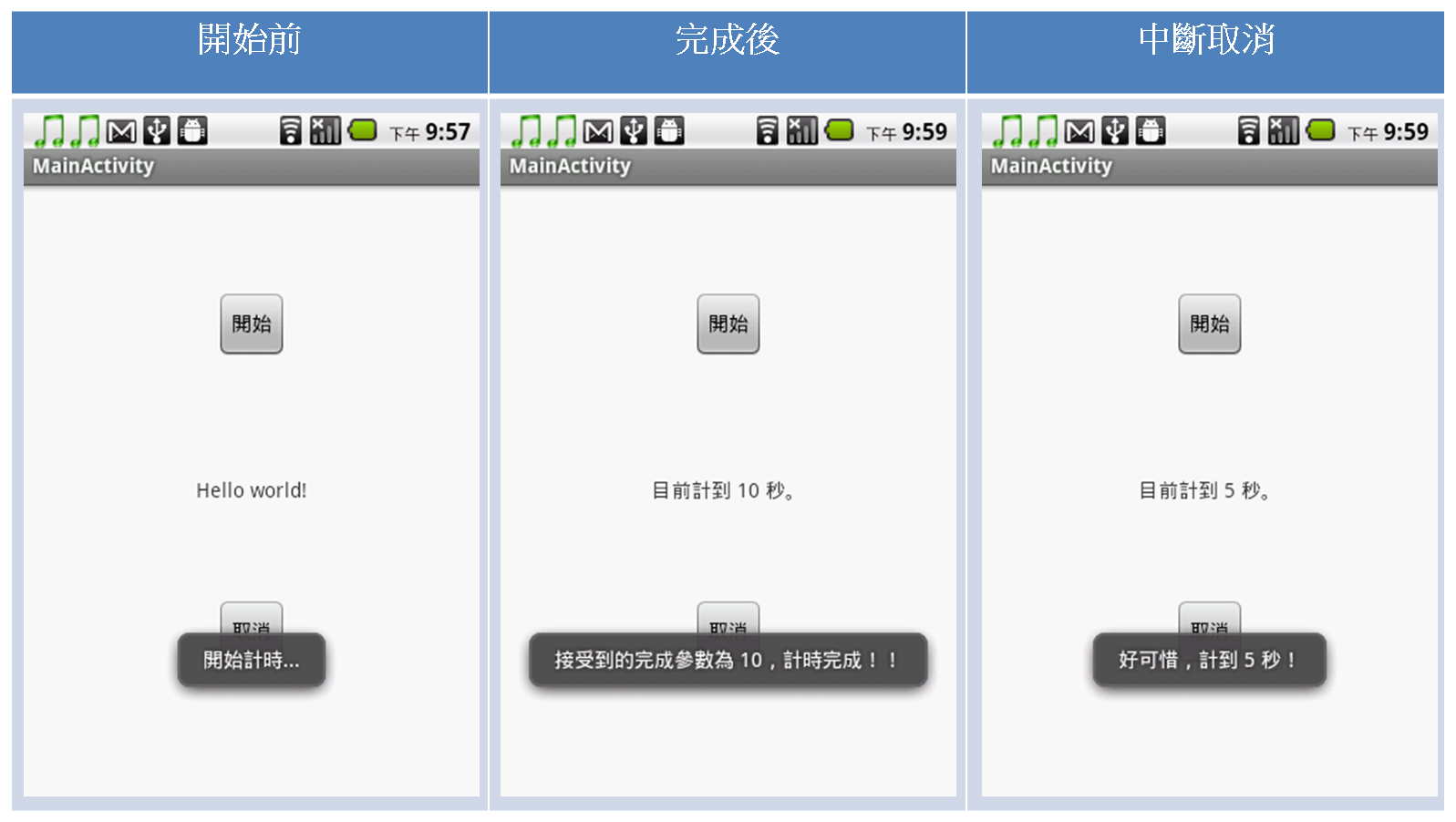
先看到 AsyncTask<Void, Integer, String>,將它想成"前"、"中"、"後"需要用到的參數而 Void 就代表不用輸入參數,待會再舉個例子,接下我們依照執行的順序排列在下方來一一介紹。 onPreExecute():處理前的動作,例如初始化某些參數或是顯示提示告訴使用者。 doInBackground(Void... arg0):實際背景處理的工作。 onProgressUpdate(Integer... values):處理過程中需要更新的動作,例如下載進度,在 doInBackground(Void... arg0) 中調用的方法為 publishProgress(values),其中參數 values 為整數陣列。 onPostExecute(String result):處理完的動作,例如提示使用者完成的訊息,或是更新介面。 onCancelled():當被取消時需要作的事,例如提示使用者任務取消,並更新介面。 那我們就來寫一個計算到 10 的計時器,但在開始算時要告訴使用者開始算了,再算的中途需要顯示目前算到幾秒,如果順利算到 10,我們就顯事任務完成,如果被取消中斷,我們就顯示好可惜,數到幾秒。 首先我們的介面設計一個顯示秒數的 TextView 及開始與取消任務的 Button。
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtCount"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:padding="@dimen/padding_medium"
android:text="@string/hello_world"
tools:context=".MainActivity" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnCancel"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/txtCount"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="60dp"
android:text="取消" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnStart"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_above="@+id/txtCount"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="73dp"
android:text="開始" />
</RelativeLayout>
接下來的非同步任務就如下:
class GoodTask extends AsyncTask<Integer, Integer, String> {
// <傳入參數, 處理中更新介面參數, 處理後傳出參數>
int nowCount;
@Override
protected String doInBackground(Integer... countTo) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 再背景中處理的耗時工作
try {
for (int i = 0; i < countTo[0]; i++) {
Thread.sleep(1000);
nowCount = i + 1;
publishProgress(nowCount);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "10";
}
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPreExecute();
// 背景工作處理"前"需作的事
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"開始計時...", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(Integer... values) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onProgressUpdate(values);
// 背景工作處理"中"更新的事
txtCount.setText("目前計到 " + values[0] + " 秒。");
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(String result) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onPostExecute(result);
// 背景工作處理完"後"需作的事
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"接受到的完成參數為 "+ result + ",計時完成!!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCancelled();
// 背景工作被"取消"時作的事,此時不作 onPostExecute(String result)
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"好可惜,計到 " + nowCount + " 秒!", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
而針對介面我們在 onCreate() 撰寫如下:
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
txtCount = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txtCount);
btnCancel = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnCancel);
btnStart = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
btnStart.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (goodTask == null) {
goodTask = new GoodTask();
goodTask.execute(10);
} else {
if (goodTask.isCancelled()
|| goodTask.getStatus().equals(AsyncTask.Status.FINISHED)) {
goodTask = new GoodTask();
goodTask.execute(10);
}
}
}
});
btnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if (goodTask != null) {
if (!goodTask.isCancelled()
&& goodTask.getStatus().equals(AsyncTask.Status.RUNNING)) {
goodTask.cancel(true);
}
}
}
});
}
可以留意再重新啟動時我都會檢查任務是否在執行中,因為我們不想有一大堆相同任務在執行,這將會造成混亂,而且我們在任務管理上也會造成不便。結果如下: 附上原始碼:http://webhd.xuite.net/_oops/u93240xx/28i
Ref : http://andcooker.blogspot.tw/2012/08/android-asynctask.html