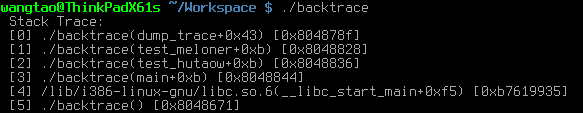
在Linux程序中輸出函數調用棧
程序發生異常時,將函數的調用棧打印出來,可以大大提高定位效率。
Linux中提供了三個函數用來獲取調用棧:
/* 獲取函數調用棧 */
int backtrace(void **buffer, int size);
/* 將調用棧中的函數地址轉化為函數名稱 並返回一個字符串數組 */
char **backtrace_symbols(void *const *buffer, int size);
/* 將調用棧中的函數地址轉化為函數名稱 並將其定入到文件中 */
void backtrace_symbols_fd(void *const *buffer, int size, int fd);
示例代碼:
#include <execinfo.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* 打印調用棧的最大深度 */
#define DUMP_STACK_DEPTH_MAX 16
/* 打印調用棧函數 */
void dump_trace() {
void *stack_trace[DUMP_STACK_DEPTH_MAX] = {0};
char **stack_strings = NULL;
int stack_depth = 0;
int i = 0;
/* 獲取棧中各層調用函數地址 */
stack_depth = backtrace(stack_trace, DUMP_STACK_DEPTH_MAX);
/* 查找符號表將函數調用地址轉換為函數名稱 */
stack_strings = (char **)backtrace_symbols(stack_trace, stack_depth);
if (NULL == stack_strings) {
printf(" Memory is not enough while dump Stack Trace! \r\n");
return;
}
/* 打印調用棧 */
printf(" Stack Trace: \r\n");
for (i = 0; i < stack_depth; ++i) {
printf(" [%d] %s \r\n", i, stack_strings[i]);
}
/* 獲取函數名稱時申請的內存需要自行釋放 */
free(stack_strings);
stack_strings = NULL;
return;
}
/* 測試函數 2 */
void test_meloner() {
dump_trace();
return;
}
/* 測試函數 1 */
void test_hutaow() {
test_meloner();
return;
}
/* 主函數 */
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
test_hutaow();
return 0;
}
源文件下載:鏈接
編譯時需要加上-rdynamic參數,以得到符號名稱,像下面這樣:
书籍推荐