server-framework
contributed by <LanKuDot>, <ktvexe>,<judy66jo>, <JonSyuGithub> ==直播錄影==
程式碼產出
預期目標
- 整理過去server-framework資料,重現並改良。
- FB討論整理
- 案例探討: 強化 server-framework 效能
- 強化 Concurrecny
- 整合 cgi-server + facebooc,設計更好的物件導向封裝
- 整合 freeboard 以提供豐富的網頁呈現,並分析過程中伺服器端的行為,提出效能改善機制
分工
閱讀 API 及提出 refactoring
- buffer:
judy66jo - async & reactor:
JonSyuGithub - protocol-server (2人):
LanKuDot、ktvexe
如何分析 server 效能
11/18 如何分析 server 效能 / youtube link ; Nov 18, 2016
文獻回顧
Introduction
server-framework 是一個以 C99 撰寫、具備 ==物件導向== 程式設計風格的伺服器開發框架。
程式碼特色部份會介紹C語言物件導向程式設計風格,或是參考「你所不知道的 C 語言」:物件導向設計篇。[name=劉亮谷] 就是將資料與實作包在一塊兒[name=LanKuDot]
由三個部份組成-
- async.c 處理工作分配與控管 thread pool。(所以很明顯的,這邊的命名是有問題的)
- reactor.c 使用
epoll管理 server 所有 file descriptor 的狀態,並負責派送工作給async.c - protocol-server.c 定義一個 server 所需要的功能,如:發送網頁內容
主程式為 httpd.c。
HTTP request & web server
一個最簡單的 Web Server 之功能包含下列三個步驟: 步驟一 : 接收瀏覽器所傳來的網址。 步驟二 : 取出相對應的檔案。 步驟三 : 將檔案內容傳回給瀏覽器。
在這個接收與傳回的過程中,所有的資訊都必須遵照固定的格式,規範這個接收/傳送格式的協定,稱為超文字傳送協定(Hyper Text Transfer Protocol),簡稱為 HTTP 協定。
HTTP 協定格式的基礎,乃是建構在網址 URL 上的傳輸方式,早期只能用來傳送簡單的 HTML 檔案,後來經擴充後也可以傳送其他類型的檔案,包含 影像、動畫、簡報、Word 文件等。
server-framework 行為
- server要處理client的連線,必須先建立socket,若要討論socket就比較涉及七層,因為socket是屬於TCP/IP的interface,之中就包含很多實作,例如:create、listen、connect、accept、send、read和write等等,像是java中就提供三種不同形態的sockets,其中簡略的介紹,可於恐龍書中Communication in Client-Server system閱讀。
- 上圖與影片中所提及的
連接port其實嚴格來說也算是socket programming的一部份,所以不另行介紹,但是要注意的是listen時的行為。[name=劉亮谷]
運作流程
- Server 啟動後先建立 socket,讓系統建立通訊端並取得其 file descriptor。
- 將這個 socket bind 到特定的位址及 port 以接收來自外部的通訊
- 透過
Async.create()建立 thread pool,準備處理來自 reactor 的工作- 每個 thread 會執行
Async.worker_thread_cycle()
- 每個 thread 會執行
listen()執行後- Accept connect
- Printing connector
- Dealing request
- Client 的 request 將由 Server 的 Reactor 先送入 Work queue 並在 pipe 寫入 one byte
- work queue 為 linked list
- worker thread 將會取得 pipe 的 one byte 負責工作 (i.e. 處理某個 client 的 request)
Async.wait(): 等待所有 thread 跳出Async.worker_thread_cycle()迴圈。並處理完剩下的工作- 或者透過TERM (ctrl+c) 進入 close()
- close(): 將結束 Reactor 內的 Async 裡的所有 Worker thread
- 或者透過TERM (ctrl+c) 進入 close()
以上皆實作在
protocol-server.c:srv_listen()[name=LanKuDot]
影片回顧
Part1
之後整合起來吧,因為正在看影片,要即時作筆記[name=LanKuDot]
- [02:00]
Epollsystem call:偵測放進epoll的 task 有沒有 ready,如果有就放到 kernel ready queue - [03:15] 收到 request 後會放一個 byte 到 pipe 及對應 task 到 work queue,讓 thread 去取用
- [04:20] pipe 是 blocking 的呼叫,寫在 while loop 中,因此 worker thread 不會到 join。利用
ctrl+c來呼叫對應的中止函式,使整個系統可以正確停止。 - [05:30] Reactor pattern
- [07:20] Async;管理 work queue 及 thread pool
async_run:將 task 放到 work queue 中,並喚醒 threadworker_thread_cycle:從 work queue 取得 task,並 consume 掉。read()是 blocking call。sched_yield():讓完成工作的 thread,釋放掉 CPU 的資源,讓其他 thread 可以運作。- 跳出迴圈後會再執行一次
perform_tasks()處理剩餘的工作
- [09:40]
set_fd_polling(),將 request 送到 epoll,並設定輪巡的間隔 - [10:30]
reactor_review():偵測 epoll queue 有多少任務要執行 (macro_WAIT_FOR_EVENTS為epoll_wait()),並將任務推到 work queue 中 - [11:20]
srv_cycle_core()監控系統及 client 連線的狀態- 如果連線銜至時間超過 timeout 則關閉連線
srv_cycle_core()也是其中一個 task,執行完後會自己推回 work queue
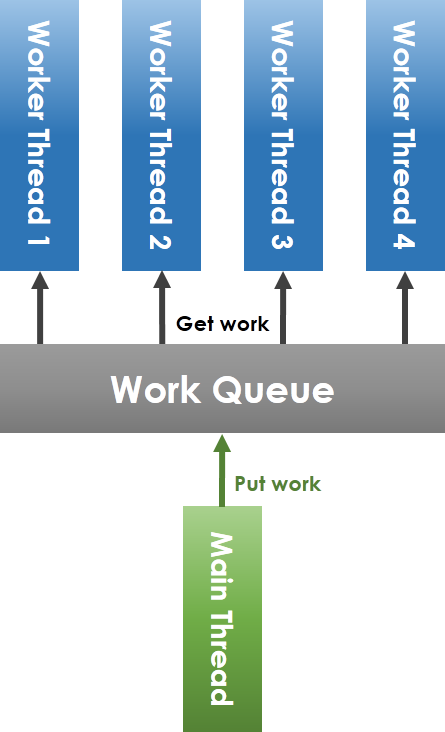
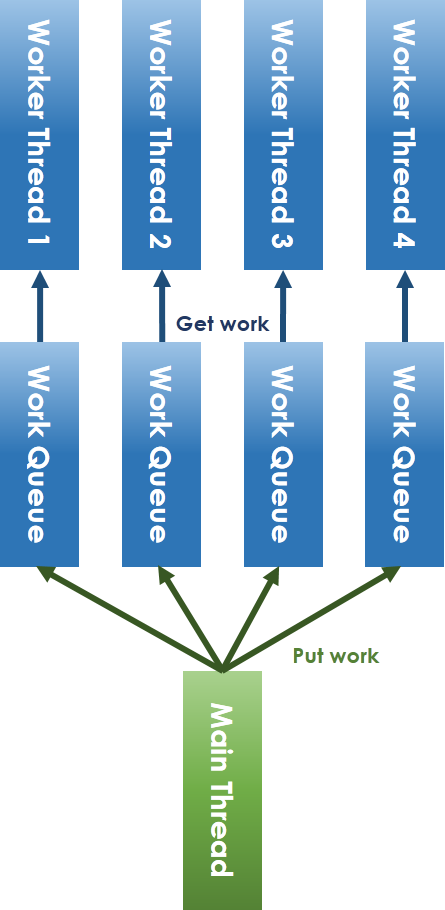
- [13:00] lock-less thread pool:所有 thread 搶同一個 work queue 改為每個 thread 有自己的 work queue。
- 用 Run Rabin 的方式配送工作到各自的 work queue
Part2
- [00:00] HTTP
- [02:40] Web Server 運作
protocal.c中的bind_server_socket()去建立 server 的 listening portstruct addrinfo紀錄 socket 所需要的資訊
- [06:10]
socket():create file descriptor for socket - [06:50]
bind():bind socket to port - [07:40]
listen():設定 socket 可以接受的最大連線數 - [09:20]
accept():取得連進來的 client 專屬的 file desciptor - [11:26]
epollsystem call:與select()和poll()不同的是在 ET mode 下只有在 fd 為 ready state 才會有反應 - [12:50]
reactor.c使用epoll()監控 - [13:30]
async.c使用pipe()取得 work queue 的工作 - [15:10]
signal()signal re-direction,改變 signal 原本的運作 - [16:29] Apache Benchmark 分析效能瓶頸與改進
- httpd.c 的
timeout設定會影響效能,但又不能只透過縮短 timeout 時間來加強效能
- httpd.c 的
- [21:31] 無論是不是 keep alive 的連線,全部都視為 not keep alive,當處理完一個 request 就關閉連線
- [23:00] 效能分析 keep alive 與否 x 優化前後
- [25:30] multi-thread 分析
- timeout 讓 thread 必須等待過時才能處理下個工作,效能無法提升
- [27:30] 將模組掛在核心上,就可以透過模組調用核心資源,直接在 kernal space 建立 socket,而不需要在複製資料到 user space
- [30:30]
server.c實作 server kernel 的行為 - [31:56] 修改前的程式流程,將 server kernel 收到的 reqeust 交給外部的
url.py處理 - [33:27] 去除繞路,直接在 server kenel 處理 request
API
Reactor
reactor 是一種 design pattern,他的概念是「同時」處理多個請求並回應,在 server-framework 用 epoll 方式實作。
昆憶哥,Design Patterns 我實在不懂,不知道 "reactor 是一種design pattern" 這句話對不對,wikipedia 有提到,我就自己揣摩了[color=blue][name=劉亮谷] 跟據 wikipedia 提到 design pattern 是一種解決常見問題的解法。design pattern 不會提供最後形式 (如:source code),而是類似 template 的存在。所以這樣解釋是對的。[name=LanKuDot]
- Reactor pattern
- Resources: 會成為系統的 input 及被系統 consume 的資源。如:client 的 request
- Synchronous Event Demultiplexer: 多對一,擋住與收集 Resource。當有 dispatcher 可以處理時,就會派送 resource 給 dispatcher。如: epoll 將收到的 client request 推到 work queue
- Dispatcher: 分派從 Demultiplexer 取得的工作到對應的 requset handler。如:將 client 待處理的 request 丟入 work queue,並喚醒 thread 處理這些 request
- Request Handler: 真正 consume request 的地方。如:worker thread 去處理工作 (client request) 也就是由 Worker thread 負責
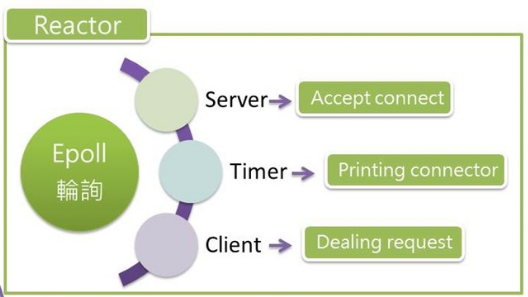
- Reactor 目的為回應 requset、使用 epoll 監控整個系統
- Server 進入 listen 階段將做三件事 Accept connect、Printing connector、Dealing request
- reactor 為 ready queue 負責接住 client 的連線要求工作
- Server: 當有 client 連線到 Server,此時 Server 工作將被設成 ready ,接受 client 連線
- Client: Client 工作將變成 ready,處理 client 的 request 並給予回應
- Timer:
API
// File: reactor.c:23
// 將一個工作存入 epoll
int set_fd_polling(int queue, // The fd of epoll
int fd, // The fd to be monitored
int action, // ADD, MOD, DEL
long milliseconds) // Scan interval
{
/* The event argument describes the object linked to the file descriptor
fd. */
struct epoll_event chevent;
/* 使得 epoll 在不同情況下可以做不同的運行 */
chevent.events = EPOLLOUT | EPOLLIN |
EPOLLET | EPOLLERR |
EPOLLRDHUP | EPOLLHUP;
if (milliseconds) {
struct itimerspec newtime;
...
timerfd_settime(fd, 0, &newtime, NULL); /* 設定 epoll 輪詢時間間隔*/
}
return epoll_ctl(queue, action, fd, &chevent); /* 將工作訊息推入 epoll */
}
// epoll 輪詢實作
// 透過 reactor_review( ) 將 epoll 中的工作抓出來執行
int reactor_review(struct Reactor *reactor)
{
if (!PRIV(reactor)->reactor_fd) return -1;
/* set the last tick */
time(&reactor->last_tick);
/* wait for events and handle them */
/* active_count 取得共有幾個工作需要被輪詢 (i.e. #(fd))*/
int active_count = _WAIT_FOR_EVENTS_; /* _WAIT_FOR_EVENTS_ macro (i.e. epoll wait system call) */
if (active_count < 0) return -1;
if (active_count > 0) {
/* for loop 完成一次的輪詢 */
for (int i = 0; i < active_count; i++) {
if (_EVENTERROR_(i)) {
/* errors are hendled as disconnections (on_close) */
reactor_close(reactor, _GETFD_(i));
} else {
/* no error, then it is an active event */
/* 從 kernel 的 read queue 取出並服務 fd */
if (_EVENTREADY_(i) && reactor->on_ready)
reactor->on_ready(reactor, _GETFD_(i));
if (_EVENTDATA_(i) && reactor->on_data)
reactor->on_data(reactor, _GETFD_(i));
}
}
}
return active_count;
}
同場加映-design pattern design pattern是對軟體設計中普遍存在(反覆出現)的各種問題,所提出的解決方案。不直接用來完成程式碼的編寫,而是描述在各種不同情況下,要怎麼解決問題的一種方案。例如:Abstract factory、Factory method、Reactor。 物件導向設計模式通常以類別或物件來描述其中的關係和相互作用,但不涉及用來完成應用程式的特定類別或物件。
原文:Object-oriented design patterns typically show relationships and interactions between classes or objects, without specifying the final application classes or objects that are involved. 看不懂"但不涉及用來完成應用程式的特定類別或物件。"這句話的意思,昆憶哥救一下。[color=blue][name=劉亮谷] 就像我上面提到的,他只是告訴你解法,但不會規定 source code 怎麼實作,反正只要能達成目的就好。[name=LanKuDot]
並非所有的軟體模式都是設計模式,設計模式特指軟體「設計」層次上的問題。還有其它非設計模式的模式,如架構模式(software architecture patterns)。同時,演算法不能算是一種設計模式,因為演算法主要是用來解決計算上的問題,而非設計上的問題。
Async
- 工作分配、控管 thread (透過 thread pool)
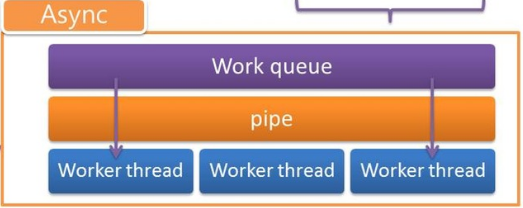
- Reactor 的 Client 工作會將處理 request 的工作丟入Work queue,並且在 pipe 寫入 one byte 紀錄
- Worker thread 若發現 pipe 有紀錄,則會將該 one byte 取出並執行 Work queue 中對應的 request
API
/* API handler*/
struct __ASYNC_API__ Async = {
.create = async_create,
.signal = async_signal,
.wait = async_wait,
.finish = async_finish,
.run = async_run,
};
/* Task Management - add a task and perform all tasks in queue */
// 處理存入 work queue 的運行,透過 pipe 喚醒 work thread 處理
static int async_run(async_p async, void (*task)(void *), void *arg) {
struct AsyncTask *c; /* work queue 採 linked list 存放,struct AsyncTask 為linked list 的 node */
...
if (async->pool) { /* async->pool 為新的 task */
c = async->pool;
async->pool = async->pool->next;
}
...
write(async->pipe.out, c->task, 1); /* 寫入 one byte 到 pipe*/
}
// thread 進入 read 將會被 block 住
// work threads 將執行此函數負責讀取 pipe 並透過 perform_tasks() 來取得 task
// 處理工作直到所有 task 被處理完 (thread 欲取得 task 時將進入 lock)
// 每個 work thread 進入 lock 取得 task 之後就會 unlock,隨後執行完 task 才會再執行第2次 while loop 請求 task
static void *worker_thread_cycle(void *_async) {
struct Async *async = _async;
char sig_buf;
/* read 就是讀取 async_run 內 wirte 的 one byte */
/* async->run 若是0則該 work thread 將被結束執行 */
while (async->run && (read(async->pipe.in, &sig_buf, 1) >= 0)) {
perform_tasks(async); /* 將 Work queue 的工作都執行完成 */
sched_yield(); /* 將此 thread 優先權降到最低 */
}
perform_tasks(async); /* 執行 Work queue 中剩餘未被執行的工作 */
...
}
當 thread 數量兩個以上將會 thread dispatching ,即使沒有 request 時 worker_thread_cycle() 內的 read(async->pipe.in, &sig_buf, 1) 仍然沒辦法 block 住 thread ? [name=JonSyuGithub]
思考這樣的 API 設計有沒有不足?或者值得做 code refactoring 之處 [name=jserv]
Refactor
IPC: pipe
- Semaphore
Protocol-Server
- 定義 server、連線收發、連線後工作狀態
Private member
struct Server
儲存 server 屬性與資料管理的 data structure
struct Server {
struct Reactor reactor; // 每個 server 都有專屬的 reactor
struct ServerSettings *setting;
struct Async *async; // Thread pool
pthread_mutex_t lock; // Server object 是會被搶的
/* 這區的 member 主要用來紀錄每個 connection 對應的資料,透過 fd 作為 offset 去存取 */
struct Protocol * volatile *protocol_map; // 聲明 `protoco_map` 是 pointer to array of pointer,而且指向的 struct Protocol 可能會被意外的改變
struct Server **server_map; // 不明
void **udata_map;
ssize_t (**reading_hooks)(server_pt srv, int fd, void *buffer, size_t size);
volatile char *busy; // Is this connection busy?
unsigned char *tout; // Timeout value of this connection
unsigned char *idle; // Idle cycle counts
pthread_mutex_t task_lock; // 搶哪個 task?
struct FDTask *fd_task_pool;
struct GroupTask *group_task_pool;
size_t fd_task_pool_size;
size_t group_task_pool_size;
void **buffer_map;
long capacity; /**< socket capacity */
time_t last_to; /**< the last timeout review */
int srvfd; // Server 用來聆聽 socket 的 fd
pid_t root_pid; // Process 的 PID
volatile char run; // Running flag
}
:::info 繼承的實現:將母 strcut 放在子 strcut 的第一個 member,透過 pointer 的 casting,可以將子 struct 視為母 struct 使用。因為母 struct 在第一個 member,當 pointer 指向子 struct 時,同時也指向母 struct。 :::
示範程式:
struct Base {
int id;
};
struct Inherit {
struct Base base;
int age;
};
int main(void)
{
struct Inherit inherit = { .base.id = 3, .age = 16 };
struct Base *base = (struct Base *)&inherit;
printf("%d\n", base->id); // 3
return 0;
}
struct FDTask
- 配送給某一個 fd (connection) 的 task,用 linked list 來管理。// 註解下的非常不好...
- Definiation:
/* the data-type for async messages */ // ^^^ bad comment ^^^ struct FDTask { struct FDTask *next; struct Server *server; int fd; void (*task)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg); // 主要派送的任務 void *arg; void (*fallback)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg); // 任務執行完要執行的工作 };
struct GroupTask
- 需要在多個 fd (connection) 執行的共同 task
- Definiation:
/* A self handling task structure */ // Self handling? struct GroupTask { struct GroupTask *next; struct Server *server; int fd_origin; void (*task)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg); void *arg; void (*on_finished)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg); unsigned char fds[]; // 要被執行的所有 task };
API
struct __SERVER_API__
-
用來 access
struct Serverobject 的 helper function,定義對於struct Serverobject 的操作。也因此struct __SERVER_API__宣告成 global const object:// protocal-server.c:237 /* Declare the corresponding handler */ const struct __SERVER_API__ Server;:::info
struct Server的 definition 是宣告在protocaol-server.c中,代表其 member 是private的,只能透過struct __SERVER_API_去 access (public member function) ::: -
__SERVER_API_大部分的函式的第一個參數都是指向struct Server物件的指標。 -
物件導向概念的實現:
Foo foo();
foo.bar(arg);
// 可以想成:
struct Foo foo;
bar(&foo, arg);
Gets and Sets
取得或設定 struct Server 的 private member
pid_t (*root_pid)(struct Server *server);
struct Reactor *(*reactor)(struct Server *server);
struct ServerSettings *(*settings)(struct Server *server);
unsigned char (*is_busy)(struct Server *server, int sockfd);
struct Protocol *(*get_protocol)(struct Server*server, int sockfd);
int (*set_protocol)(struct Server *server, int sockfd, struct Protocol *new_protocol);
void *(*get_udata)(struct Server *server, int sockfd);
void *(*set_udata)(struct Server *server, int sockfd, void *udata);
void (*set_timeout)(struct Server *server, int sockfd, unsigned chat timeout);
reactor 與 settings 允許外部直接存取 private 的 member
對應的 handler
const struct __SERVER_API_ Server = {
.root_pid = root_pid,
.reactor = srv_reactor,
.settings = srv_settings,
.is_busy = is_busy,
.get_protocol = get_protocol,
.set_protocol = set_protocol,
.get_udata = get_udata,
.set_udata = set_udata,
.set_timeout = set_timeout,
}
// 設定並取得運行 server process 可以開啟的最大 file descriptor 數量
long (*capacity)(void);
.capacity = srv_capacity;
-
使用 static variable
flim來紀錄允許使用的最大 file descriptor 數量,當該值非零時,會直接回傳該值。 -
透過預估每個 connection 會使用到的記憶體空間 (stack 與 heap) 與該 process 可以取得的記憶體空間,以計算可以容納多少 conenction。
-
實作細節
- 透過 system call
getrlimit()與setrlimit()取得指定的 resource 限制。設定以下 resource 的最大值:
struct rlimit { rlim_t rlim_cur; /* Soft limit,kernel 限制的數量 */ rlim_t rlim_max; /* Hard limit (ceiling for rlim_cur),真正可以到達的最大數量 */ }-
RLIMIT_NOFILE:該 process 可以開啟的最大 file descriptor 數量。將rlim_cur設為與rlim_max一樣,並取得設定後的值。如果設定後的rlim_cur比_SC_OPEN_MAX - 1或OPEN_MAX - 1大的話,就更新flim的值作為可以開啟的最大 fd 數。 -
RLIMIT_STACK:process stack size in bytes。- 計算一個 connection 需要多少空間:
- 19 bytes 的基本資料 mapping
- 假設 2kb 的空間給 IO buffer 和管理 request
- 然後要切齊 page 所以就弄了 4kb 給一個 connection.....
- 所以一共要
flim* 4096 bytes 的空間
call stack、thread 自己的 stack 應該也要考慮? 代表不太可能在配置的 stack 中開好開滿到自己想要的 connection 數量[name=LanKuDot]
- 嘗試配置
flim* 4096 bytes 的 stack size,設置後取得真正可以配置的 fd 數量,存到flim。
- 計算一個 connection 需要多少空間:
-
RLIMIT_DATA:process data segment size。Data segment 包含 initialized variables, uninitizlized variables 及 heap。 C programming memory layout[name=LanKuDot]
- 為每個 connection 配置 24kb 的 data segment,並取得真正可以配置的空間,得到最後可以使用的 fd 數。
- 24 kb 也沒有根據QQ
- 透過 system call
Server 控制
// 啟動 server,啟動資訊在 struct ServerSettings 中
// 此函式會將 main threaad block 住,直到 server 停止
int (*listen)(struct ServerSettings);
.listen = srv_listen;
- 實作細節
- 先檢查傳入的
struct ServerSettings的資料是否有效,否則會使用預設值:protocol:不能為NULL,否則直接回傳錯誤
FIXME 註紀要輸出 warning message,用
assert會不會太暴力?[name=LanKuDot] 太暴力的意思是希望只 warning ,但不 suspend 掉嗎? [name=亮谷] 不過如果這是無法透過預設來處理的話,直接強制關閉也是可以[name=LanKuDot][color=green]port:8000timeout:5threads:1processes:1
- 建立與初始化
strcut Serverprotocol-server.c:648- 透過
srv_capacity()計算最大連線數,以此建立所需的資料數量 - 建立一個
struct Serverobject 紀錄 server 的資訊,及儲存上一步所建立的資料的 pointer - 初始化資料
srv_fd:透過bind_server_socket()取得lock,task_lock:透過pthread_mutex_init()初始化task_pool,group_task_pool:設為空 pollserver_map[i]:存自己的 reference (類似this)buffer_map[i]:透過Buffer.create()取得protocol_map[i],busy[i],idle[i],tout[i],udata_map[i]:設為 0- handlers of reactor:
.reactor.maxfd = capacity - 1, .reactor.on_data = on_data, .reactor.on_ready = on_ready, .reactor.on_shutdown = on_shutdown, .reactor.on_close = on_close,
- 設定 signal 的行為。參照
探討 epoll, pipe, signals 等系統呼叫的SIGNAL一節 - 依
settings.processesfork processsrv.root_pid紀錄 root process 之 pid- 只有 root process 會紀錄所有 child processes 的 pid
- 先檢查傳入的
// 停止指定的 server `server`
void (*stop)(struct Server *server);
.stop = srv_stop;
// 停止所有 server
void (*stop_all)(void);
.stop_all = srv_stop_all;
Socket (Client coonnection) 控制
// 註冊新的 connection 到 server 及 protocol 管理系統
int (*attach)(struct Server *server, int sockfd, struct Protocol *protocol);
.attach = srv_attach;
// 關閉連接,只有在該連線的資料傳送完畢時,才會正確關閉
void (*close)(struct Server *server, int sockfd);
.close = srv_close;
// hijack:挾持,從 server 手上搶奪這個 connection 的控制權。
// server 在傳送完這個 connection 的資料之前
// 會 block 住這個 function call
int (*hijack)(struct Server *server, int sockfd);
.hijack = srv_hijack;
// 取得指定 protocol 的連線數量
// 如果 service 為 NULL,則將所有 protocol 納入計算
long (*count)(struct Server *server, char *service);
.count = srv_count;
// 操作指定的 connection,使其重置 timeout counter
void (*touch)(struct Server *server, int sockfd);
.touch = srv_touch;
Read and Write hook
- 每一個 socket 都有專屬的 hook
- 只有在 invoke read 或 write function (如:
Server.read或Server.write) 才會執行,以取代read()或write() - 目的在於讓欲傳送的資料作前處理 (如可以支援 SSL/TLS),或是將收到的資料作後處理
- 對於 writing hook 的實作規定:
- 必須帶有參數:
- pointer to server (buffer owner)
- pointer to socket
- pointer to data to be written
- length of data
- 回傳:
- 從 buffer 寫入的 byte 數,非實際寫到 socket 的 bytes 數
- -1:如果資料無法被傳送
- 0:如果沒有資料傳送,但 connection 應該要維持開啟而且沒有遭遇內部錯誤
- 必須真的有傳送資料到 network,否則 writing hook 不會再次被呼叫
- 必須帶有參數:
- 對於 reading hook 的實作規定:
- 與 writing hook 相似,但 length of data 指定要讀取的 byte 數
- 回傳實際寫入 buffer 的 bytes 數
// 設定 connection 對應的 reading 及 writing hook
void (*rw_hooks)(server_pt srv, int sockfd,
ssize_t (*reading_hook)(server_pt srv, int fd,
void *buffer, size_t size),
ssize_t (*writing_hook)(server_pt srv, int fd,
void *data, size_t len));
.rw_hooks = rw_hooks,
// reading 及 writing hook template
ssize_t (*read)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, void *buffer, size_t max_len);
.read = srv_read,
size_t (*write)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, void *data, size_t len);
.write = srv_write,
// 另外提供三種變種
// 直接將 data pointer 指向 `data`
ssize_t (*write_move)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, void *data, size_t len);
.write_move = srv_write_move,
// 盡快將資料送出,不希望等待
ssize_t (*write_urgent)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, void *data, size_t len);
.write_urgent = srv_write_urgent,
ssize_t (*write_move_urgent)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, void *data, size_t len);
.write_move_urgent = srv_write_move_urgent,
// 傳欉一整個指定的檔案,就好像是一個 atomic 的 package
// 實際上是一個一個 chunk 送出去
ssize_t (*sendfile)(server_pt srv, int sockfd, FILE *file);
.sendfile = srv_sendfile,
Task and Thread pool
- 非同步 task:並非在呼叫該函式時就會執行的 task,而是被編入排程,等待被執行
// 指定要跑在除了 `origin_fd` 的非同步 task
// 當指定的 task 執行完後,會呼叫 `on_finish`
int (*each)(struct Server *server, int origin_fd,
char *service,
void (*task)(struct Server *server, int target_fd, void *arg),
void *arg,
void (*on_finish)(struct Server *server, int origin_fd, void *arg));
// 指定要跑在除了 `fd_originator` 的 task
// task 會依序跑在所有 connection,而且會 block 住
int (*each_block)(struct Server *server, int fd_originator,
char *service,
void (*task)(struct Server*server, int fd, void *arg),
void *arg);
// 指定要跑在某個 conection 上的非同步 task
int (*fd_task)(struct Server *server, int sockfd,
void (*task)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg),
void *arg,
void (*fallback)(struct Server *server, int fd, void *arg));
// 指定多久後執行該 task,執行完後該 task 就結束
// 會多使用一個 fd 給 timer
int (*run_after)(struct Server *self, long milliseconds, void task(void *), void *arg);
// 與 `run_after` 相似,但可以指定要執行這個 task 幾次。
// 如果 `repetitions` 為 0,則永遠重複執行
int (*run_every)(struct Server *self, long milliseconds, int repetitions, void task(void *), void *arg);
// 用來監控整個系統工作狀態,決定工作是否中斷連線/執行
static void srv_cycle_core(server_pt server)
再者來聊聊 struct Protocol 與 struct ServerSettings
在 protocol-server.h 中,有段 macro start_server,這邊用到技巧稱為 Variadic Macros ,這種宣告方式允許 macro 像 function call 一樣能有多個參數。 可參考:Variadic Macros - The C Preprocessor - GCC - GNU
#define start_server(...) \
Server.listen((struct ServerSettings){__VA_ARGS__})
所以從上方 macro 可以得知 start_server 的參數為 ServerSettings 的 member 。
setting server
固接下來開始來研究 ServerSettings 中的 member 。
char *port顧名思義是用來設定 socket 時所使用的 port ,在protocol-server.c中srv_listen()會將其 default 設成8080。
本來想來介紹一下 port 8080 的用途,但我發現查完資料後還是不太理解,大致內容為 8080 與 80 port 為負責http traffic 。 [name=亮谷][color=blue]
-
char *address同理為設定 IP address 用,他的使用在protocol.c中bind_server_socket(),他使用到 linux system callgetaddrinfo()。 -
getaddrinfo()為給定 host IP 與 port/http ,他會回傳addrinfostructures 其中已填好 Internet address 的資訊, 可用於bind()、connect()。 可參考:Linux Programmer's Manual GETADDRINFO(3) -
threads、processes、timeout在前面影片回顧有做過整理,分別是用來設定 thread pool 的 thread 數量、並行的 process 數量、 worker thread 每次要等待的時間。
struct ServerSettings {
char *port; /**< the port to listen to. default to 8080. */
char *address; /**< the address to bind to. Default to NULL
(all localhost addresses). */
int threads;
int processes;
unsigned char timeout;
}
除了上方的 member data 外,在 server-framework 中多次提及的以 function pointer 實作物件導向,所以接下來分析各 function pointer 指向之功能。
void (*on_init)(struct Server *server);
void (*on_finish)(struct Server *server);
void (*on_tick)(struct Server *server);
void (*on_idle)(struct Server *server);
void (*on_init_thread)(struct Server *server);
char *busy_msg; /**< C-style string indicating the server is busy.
default to NULL, which means simple disconnection
without messages. */
void *udata; /**< opaque user data. */
protocol
char *service; /**< a string to identify the protocol's service
such as "http". */
void (*on_open)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when a connection is opened. */
void (*on_data)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when a data is available. */
void (*on_ready)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when the socket is ready
to be written to. */
void (*on_shutdown)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when the server is shutting
down, but before closing the
connection. */
void (*on_close)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when connection was closed. */
void (*ping)(struct Server *,
int sockfd); /**< called when the connection's timeout
was reached. */
Refactor
struct __SERVER_API__
- 有些函式使用
struct Server *有些寫server_pt來指向struct Server物件。雖然有typedef,但統一使用一種會比較好 -
count()的 argumentservice只指定要查詢的 protocol,或許用service_protocol比較好 -
run_after()與run_every()的 comment 不佳run_after():run a task aftermillisecondsmsrun_every():run a task everymilliseconsand repeatrepetationstimes
struct Protocol
struct ServerSettings
Buffer
API
// 建立 buffer,buffer 將負責接收 client 送到 server 的 request 封包
// 提供給 protcol-server 初始化時,會呼叫 capacity 次 Buffer.create(&srv) 來建立 capacity 個 buffer
// 當 server 開始處理該 request (i.e. 讀取 request 對應的 file) 後將寫入 file 到該封包並回傳給 client
static inline void *create_buffer(server_pt owner)
// 釋放掉 buffer
// 提供給 protocol-server 於結束程式時,能將初始化時所建立 capacity 個 buffer (i.e. buffer_map[0~capacity]) 給 free 掉
void destroy_buffer(void *buf)
- type volatile 避免程式在 I/O 和 multithread program 時自動優化,只讀取一次具有揮發性的變數
探討 epoll, pipe, signals 等系統呼叫
Epoll
monitoring multiple file descriptors to see if I/O is possible on any of them. The epoll event distribution interface is able to behave both as edge-triggered (ET) and as level-triggered (LT).
- 非同步 I/O,解決因大量連線造成 process 和 thread 無法 handle的狀況
- 能 handle 比 select 更多連線,且非線性掃描,但只能在 linux 系統上運作
- ET(edge-triggered):只有在 fd 變成 ready-state 時有反應,直到事件結束後又發生下一次,如此一來就不用一直詢問一些不活躍的 connect
// 生成epoll
int epoll_create(int size)
int epoll_create1(int flags)
// 新增或移除監聽的fd或更改fd的監聽選項
int epoll_ctl(int epfd, int op, int fd, struct epoll_event *event)
// 回傳ready的fd的數量,把fd存在events array中
int epoll_wait(int epfd, struct epoll_event *events,int maxevents, int timeout)
PIPE
- 單向傳輸的 IPC 資料流,有兩個端口 fd,一個是 read-only,一個是 write-only
- 當嘗試 read 一個空的 pipe 時,會被 block 住,當嘗試寫入 full的 pipe 時,write 會被 block
// 生成 pipe,將 read, write 端 fd 存入 array
int pipe(int pipefd[2])
// 將 count bytes 的資料寫入 pipe_write_end
ssize_t write(int fd, const void *buf, size_t count);
// 從 pipe_read_end 讀 count bytes 的資料
ssize_t read(int fd, void *buf, size_t count);
- 只需要一個 API,但是其只適用於 parent process 與 child process
- 用法說明:
- 使用 pipe() 建立兩個 file descripter,第一個 FD 用來從PIPE讀取資料,第二個FD 用來作為寫入資料至PIPE,如下例:
#include<unistd.h>
int fds[2];
int pipe(fds);
- 接著呼叫 fork ,因為child process 會擁有同樣的 FD,因此便可以透過這兩個 FD 進行溝通
SIGNAL
- 接收訊號後改變原本動作,確保server正確執行與結束
// 改變動作
int sigaction(int signum, const struct sigaction *act, struct sigaction *oldact);
// The sigaction structure
struct sigaction {
void (*sa_handler)(int); // Handler。與 sa_sigaction 擇一設定即可。sa_handler 可以為 SIG_DEL (default)、SIG_IGN (Ignore)、或自定義的函式
void (*sa_sigaction)(int, siginfo_t *, void *);
sigset_t sa_mask; // 執行 handler 時要忽略哪些訊號
int sa_flags; // 改變 signal 的行為
void (*sa_restorer)(void);
};
- signum 輸入參考
Signal Value Action Comment
──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
SIGINT 2 Term Interrupt from keyboard
SIGKILL 9 Term Kill signal
SIGPIPE 13 Term Broken pipe: write to pipe with no readers
SIGTERM 15 Term Termination signal
- 在 server-framework 中將 SIGINT、SIGTERM 導向到
on_signal();忽略 SIGPIPE 訊號
其他討論
-pthread vs -lpthread
效能測試
apache ab
2016q1 Homework #3中提到以ab -c 32 -n 100 http://localhost:8080/測試 server frameworks 效能,看到apache docs 中的描述: :::info ab is a tool for benchmarking your Apache Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) server.
-c concurrency Number of multiple requests to perform at a time. Default is one request at a time.
-n requests Number of requests to perform for the benchmarking session. The default is to just perform a single request which usually leads to non-representative benchmarking results. ::: 所以說,這邊的測試方式是,對 Web Server 送出100個 request ,且一次送出32次 request。 看到結果:
Web server-
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 33
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 33
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
- Connection to FD: 33
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 32
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 0
# Total Clients: 0
Clients: 29
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 29
- Connection to FD: 33
- Connection to FD: 32
Clients: 29
Benchmark-
Server Software:
Server Hostname: localhost
Server Port: 8080
Document Path: /
Document Length: 13 bytes
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 16.167 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 0
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 6.19 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 5173.529 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 161.673 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 0.60 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 0 1 0.2 1 1
Processing: 3999 4053 78.6 4000 4168
Waiting: 0 0 0.2 0 1
Total: 4000 4054 78.5 4000 4168
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 4000
66% 4000
75% 4167
80% 4167
90% 4168
95% 4168
98% 4168
99% 4168
100% 4168 (longest request)
FB討論-ab 測試
問題描述: 為什麼 httpd 可以用 ab 測出結果,但是 test-reactor 在 ab test 的時候卻會 timeout? 如果是測 test-reactor 的話會出現這個訊息: Benchmarking 127.0.0.1 (be patient)...apr_pollset_poll: The timeout specified has expired (70007)
原因探討: epoll 本身沒有 socket 的 timeout, 讓 socket 接上去關不起來,新增一個 list 存放每個 fd 的 time,然後在 epoll_wait return 0的時候去檢查有沒有 timeout, timeout 的話就把 socket 關掉。這樣做之後 ab 就有結果了。 可是這樣做就捨棄 epoll 的好處了,變成還要去維護一個 timeout 的 list,每次都要去 iteration 一次,跟 select 與 poll 相去不遠矣。
除此之外的作法還有,想想是否是每次 epoll 的回傳都要檢查 timeout list,或是新增一個 timer,定時去檢查就好 (後面就會看到了) 或是想辦法讓 ab 自己去關閉這個 socket 的連線,當然需要靠我們提供資訊 (Content-Length),client 端才知道這次的 request 已經回復完畢
==apache bench的問題== by < Broken Performance Tools >
- Single thread limited (use wrk for multi-threaded)
wrk是一個modern HTTP 效能分析工具,重點是他可以用於single multi-core CPU上,不過有看到資料說wrk只能執行於Unix like的系統上,這點我還沒有進行確認,僅先進行紀錄。 附上README片段: wrk is a modern HTTP benchmarking tool capable of generating significant load when run on a single multi-core CPU. It combines a multithreaded design with scalable event notification systems such as epoll and kqueue.[name=劉亮谷][color=blue]
- Keep-alive option (-k): - without: Can become an unrealistic TCP session benchmark - with: Can become an unrealistic server throughput test
- Performance issues of ab's own code
這個問題雖然不難理解,不過很難想像解決的辦法,畢竟任何的benchmark tool一定也具有本身的overhead。[name=劉亮谷][color=blue]
效能瓶頸
實驗與實作
重現實驗
In http.c:
- 更改 epoll polling 的時間,將原先 1000ms 改為 1ms,結果 Requests per second 提升至8.76 [#/sec]
void on_init(server_pt srv)
{
Server.run_every(srv, 1, -1, (void *) timer_task, srv);
}
Server Software:
Server Hostname: localhost
Server Port: 8080
Document Path: /
Document Length: 13 bytes
效能:
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 11.413 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 1
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 1, Exceptions: 0)
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 8.76 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 3652.058 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 114.127 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 0.85 [Kbytes/sec] received
不太確定上面你們想怎麼排版 所以就麻煩自行更改囉~ [color=red][name=課程助教]
- 再來更改 epoll 的 timeout,原先設定為 2,代表每次的等待時間為 2 秒,超過則離開,改詢問下個工作,將其降為 1 秒。 結果 Requests per second 提升至 13.08 [#/sec]
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct Protocol protocol = { .on_data = on_data };
start_server(.protocol = &protocol,
.timeout = 1,
.on_init = on_init,
.threads = THREAD_COUNT);
return 0;
}
結果:
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 7.644 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 5
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 5, Exceptions: 0)
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 13.08 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 2446.082 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 76.440 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 1.26 [Kbytes/sec] received
In protocol-server.c 由於上方實驗可發現,timeout 會影響效能,所以在 trace protocol-server.c 時想到,理論上這次實驗中資料的傳輸應該是遠比 timeout 所設定的時間還要都來的短,既然如此在資料傳輸結束時關閉 connection 應該能提升效能。
TODO:驗證正確性[name=亮谷][color=blue]
static void async_on_data(server_pt *p_server)
{
......
(*p_server)->idle[sockfd] = 0;
protocol->on_data((*p_server), sockfd);
// release the handle
(*p_server)->busy[sockfd] = 0;
+ if ((*p_server)->protocol_map[sockfd]->service != timer_protocol_name) {
+ reactor_close(_reactor_(*p_server), sockfd);
+ }
return;
}
效能: 會發現 Requests per second 很浮動,可以發現這個作法效能受到資料傳輸速度的影響極大,所以應該不是好的改善方式。
傳輸完就關掉的話,重新連線會不會有 latency 呢? 有沒有方法可以確認這次傳輸是最後一筆資料。[name=LanKuDot][color=blue]
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 0.013 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 0
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 7683.44 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 4.165 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.130 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 742.83 [Kbytes/sec] received
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 0.008 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 0
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 12090.44 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 2.647 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.083 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 1168.90 [Kbytes/sec] received
In reactor.c
int reactor_review(struct Reactor *reactor)
{
if (!PRIV(reactor)->reactor_fd) return -1;
/* set the last tick */
// time(&reactor->last_tick);
struct timeval tv;
gettimeofday(&tv,NULL);
reactor->last_tick = (tv.tv_sec)*1000 + (tv.tv_usec)/1000;
/* wait for events and handle them */
int active_count = _WAIT_FOR_EVENTS_;
if (active_count < 0) return -1;
這部份做了什麼修改呢?[color=red][name=課程助教]
結果:
Server Software:
Server Hostname: localhost
Server Port: 8080
Document Path: /
Document Length: 13 bytes
Concurrency Level: 32
Time taken for tests: 0.017 seconds
Complete requests: 100
Failed requests: 3
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 3, Exceptions: 0)
Total transferred: 9900 bytes
HTML transferred: 1300 bytes
Requests per second: 5841.12 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 5.478 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 0.171 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 564.72 [Kbytes/sec] received
實做與分析 lock-less thread pool
- 在使用多執行緒的程式中,為了避免多個執行緒同時對一個變數進行讀寫的動作( race condition),會使用 mutex_lock 結合 condition variable。然而在 mutex_lock 的取得及釋出上,有不小的成本。
- 執行緒從一個 work queue 中,去搶(競爭)工作來做,為了避免多個執行緒重複執行同一個工作,在取得工作時都必須以 mutex_lock 將執行緒的執行堵塞住。
- 為了降低 mutex_lock 的使用次數,意味著要降低資源競爭的情況。而為了降低資源競爭的情況,可以將單一個 work queue,改成每一個執行緒都有自己的 work queue,這樣一來每一個執行緒只要從自己的 queue 中拿工作來做,以避免執行緒間搶工作時必須使用 mutex_lock。
- 修改Async的實做
- 改變
struct Async原本使用 structure membertasks作為 work queue,儘管 memberthreads的註解寫著 thread pool 但並沒有實質用處。
/** The Async struct */
struct Async {
pthread_mutex_t lock; /**< a mutex for data integrity */
struct AsyncTask * volatile tasks; /**< work queue*/
struct AsyncTask * volatile pool; /**< a pool recycling the task node*/
struct AsyncTask ** volatile pos; /**< the position for new tasks: rear of work queue */
...
/** the thread pool */
pthread_t threads[];
};
- 所以在新的實做中,我們移除了與原本 work queue 相關的 structure member,並以
struct thpool threads取代原本的pthread_t threads:
struct thpool {
pthread_t thid; /**<pthread id*/
struct AsyncTask work_queue[WORK_QUEUE_SIZE]; /**<work queue simple ring buffer*/
/** The pipe used for thread wakeup */
struct {
int in; /**< read incoming data (opaque data), used for wakeup */
int out; /**< write opaque data (single byte),used for wakeup signaling */
} pipe;
unsigned int rear; /**<the place to get the tasks*/
unsigned int front; /**<the place to put new tasks*/
};
- 將工作加入執行緒所對應的 work queue
- 在原先的實做中,並不像上面的圖,會有一個 main thread( root thread)將工作一一分配至每個work queue中,queue 裡的工作來源是由執行緒目前執行的某些工作透過
Async.run產生新的工作。 - 對於這些會產生新工作的生產者如
srv_cycle_core,我們額外以一個執行緒來執行:
- 在原先的實做中,並不像上面的圖,會有一個 main thread( root thread)將工作一一分配至每個work queue中,queue 裡的工作來源是由執行緒目前執行的某些工作透過
// function: async_create(int threads)
async_p async = malloc(sizeof(*async) + (threads+1) * sizeof(struct thpool));
/**< an extra thread is used to be producer */
- 而其餘的工作則是透過 Round-Robin 安排至其他執行緒的 work queue 中:
if(flag == 1) return dispatch_task(async, async->threads+async->count, task, arg) ;
thread = RR(async);
return dispatch_task(async, thread, task, arg);
- 排程與加入工作到 work queue 時,為了避免多個執行緒同時執行排程並加入工作到 work queue 中,我們使用 atomic operation 以確保變數遞增時的同步:
cur_thread_index = __sync_add_and_fetch(&cur_thread_index,1) %async->count;
c = thread->work_queue + queue_offset(__sync_fetch_and_add(&(thread->front),1));
- 執行 work queue 中的工作 保留原本實做中使用 pipe 喚醒等待工作的執行緒的方式來執行 work queue 中儲存的工作,每次執行 work queue 中的工作,會作到 queue 變成空為止:
// function: perform_tasks(async_p async)
do {
/* grab a task from the queue. */
if(thread_queue_empty(thread)) break;
tmp = thread->rear++;
c = thread->work_queue + queue_offset(tmp);
/* perform the task */
if (c->task) c->task(c->arg);
} while (c);